💿 Software Installation
Download and install Arduino IDE
First, go to the software page on Arduino.cc site. For this section, download the correct version according to you operating system.

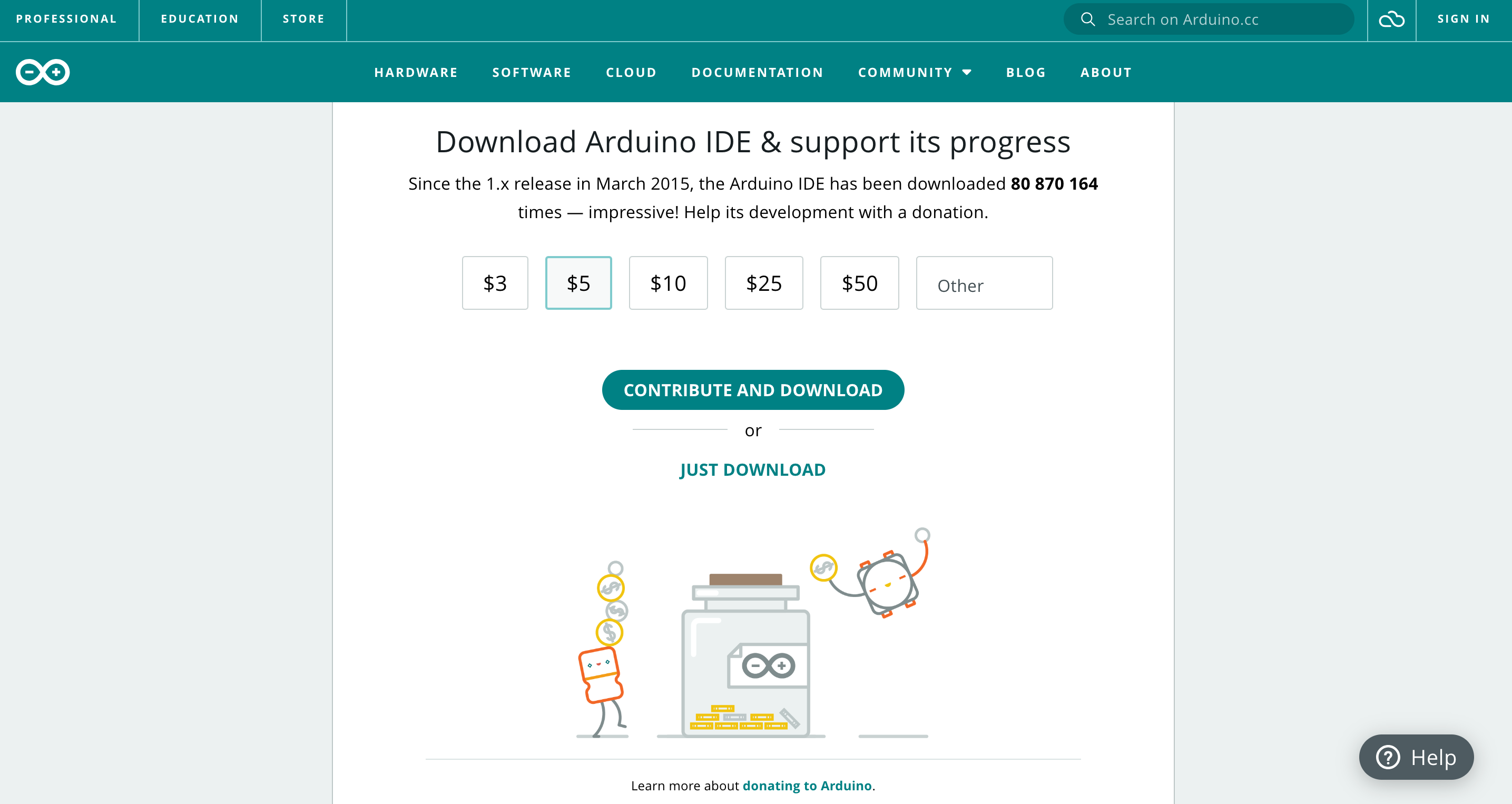
After choosing to download the Arduino IDE for your operating system, you'll be presented with a window like the one shown below. From here, simply click on "Just Download" to initiate the download process.
Note: If you encounter any issues with your operating system version and Arduino IDE downloads, please visit the official Ardunio page: Arduino Download IDE.
Once the download and installation process is successfully completed, launch the program. You will encounter a program like the one showed below. Note that the filename and version number of the launched sketch might be different, which is not a problem.
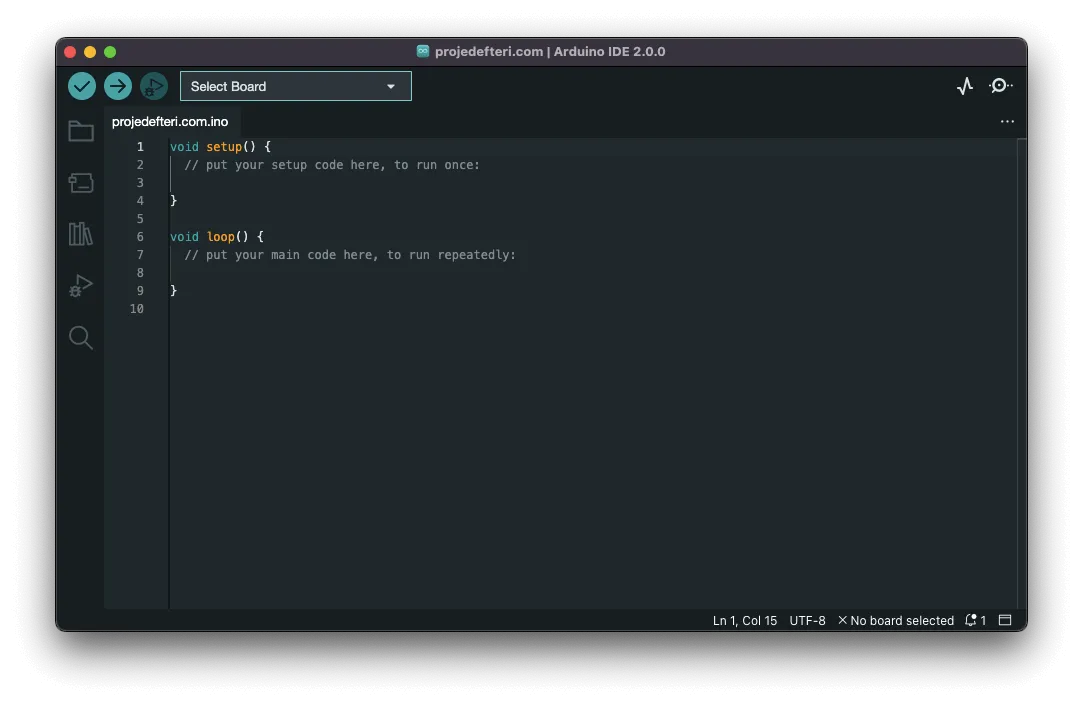
Congratulations! 🎉 You've successfully installed the program. Now you're ready to configure your IDE and start coding! Great job 😃
Download and install OpenMV IDE
OpenMV is only needed for use Case Flower (Image) classification.
First, go to the OpenMV IDE download page to download the correct version for your Operating System, and follow the instructions for its installation on your computer.
The IDE should open, defaulting to the helloworld_1.py code on its Code Area. If not, you can open it from Files > Examples > HelloWord > helloword.py
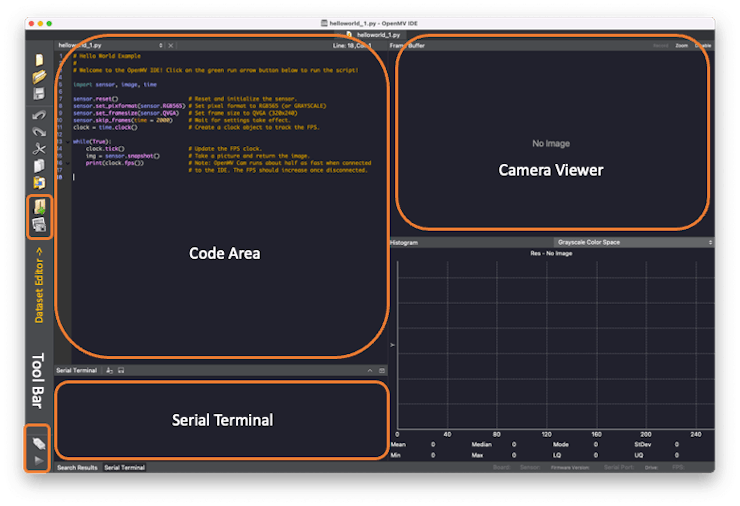
Any messages sent over a serial connection, including output from print() statements or error messages, will appear in the Serial Terminal during runtime. Images captured by the camera will be shown in the Camera Viewer area (or Frame Buffer), with a corresponding histogram displayed directly below the Camera Viewer.
OpenMV IDE is the primary integrated development environment for working with OpenMV Cameras and Arduino Pro boards. It offers a robust text editor, a debugging terminal, and a frame buffer viewer with a histogram display. In this setup, we’ll use MicroPython to program the Nicla Vision.
Before connecting the Nicla to OpenMV IDE, make sure it has the latest bootloader version. Open Arduino IDE, select the Nicla board, and navigate to Examples > STM_32H747_System > STM32H747_manageBootloader to open the sketch. Upload the code to the board, and follow the instructions provided in the Serial Monitor.
After updating the bootloader, put the Nicla Vision into bootloader mode by double-pressing the reset button on the board. The green LED will begin to fade in and out. Then, return to OpenMV IDE and click the connect icon on the left toolbar.
A pop-up will appear, indicating that a board in DFU mode has been detected and prompting you to choose how to proceed. Select "Install the latest release firmware (vX.Y.Z)" to install the latest OpenMV firmware on the Nicla Vision.
You can leave the option Erase internal file system unselected and click [OK].
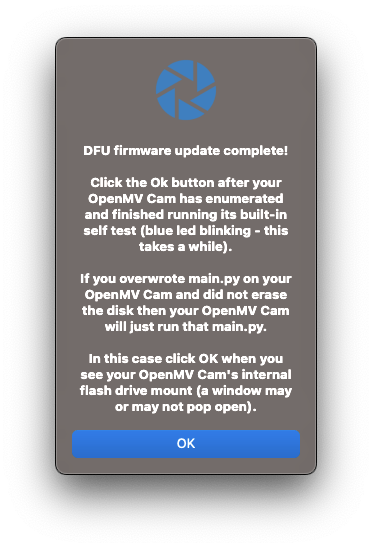
The Nicla's green LED will start flashing as the OpenMV firmware is uploaded to the board. A terminal window will open, displaying the progress of the firmware installation.
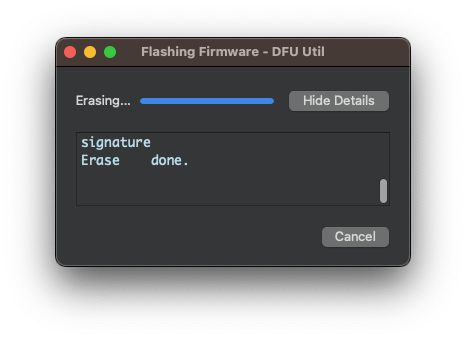
Wait until the green LED stops flashing and fading. When the process ends, you will see a message saying, “DFU firmware update complete!”. Press [OK].
A green play button appears when the Nicla Vison connects to the Tool Bar.
Also, note that a drive named “NO NAME” will appear on your computer.:
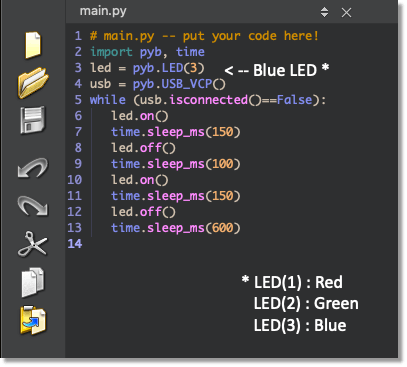
This code is the “Blink” code, confirming that the HW is OK.
To test the camera, run helloworld_1.py. Select the script by navigating to File > Examples > HelloWorld > helloworld.py.
Click the green play button to upload and run the MicroPython script (helloworld.py) from the Code Area on the Nicla Vision. The Camera Viewer will display the video stream, and the Serial Monitor will show the FPS (frames per second), which should be around 14 fps.
The image is taken from Use Case nr.3 to show the display only running snapshots from the camera.
Here is the helloworld.py script:
# Hello World Example 2
#
# Welcome to the OpenMV IDE! Click on the green run arrow button below to run the script!
import sensor, image, time
sensor.reset() # Reset and initialize the sensor.
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # Set pixel format to RGB565 (or GRAYSCALE)
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QVGA) # Set frame size to QVGA (320x240)
sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) # Wait for settings take effect.
clock = time.clock() # Create a clock object to track the FPS.
while(True):
clock.tick() # Update the FPS clock.
img = sensor.snapshot() # Take a picture and return the image.
print(clock.fps())
The code can be split into two parts:
-
Setup: Where the libraries are imported, initialized and the variables are defined and initiated.
-
Loop: (while loop) part of the code that runs continually. The image (img variable) is captured (one frame). Each of those frames can be used for inference in Machine Learning Applications.
To interrupt the program execution, press the red[X] button.
Note: OpenMV Cam runs about half as fast when connected to the IDE. The FPS should increase once disconnected.